What is LDPE?
Types, Grades, and Applications
Introduction Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is one of the most widely used industrial polymers due to its high flexibility, excellent chemical resistance, and easy processability. In this article, we will explore the types of LDPE, its grades, applications, advantages, and disadvantages, providing you with comprehensive information.
Table of Contents
ToggleLDPE Characteristics
High flexibility and good impact resistance
Chemical resistance, making it non-reactive with many acids and bases
Easy processability for manufacturing various plastic products
Relative transparency, allowing its use in different packaging applications
High resistance to cracking
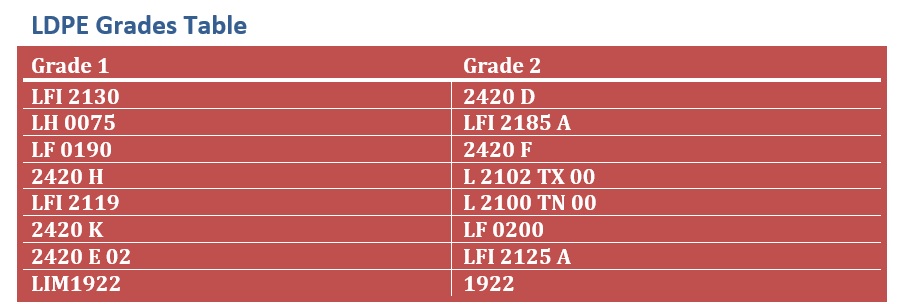
LDPE Grades and Applications
LDPE is available in various grades, each designed for specific applications:
1. General Purpose LDPE
Used in plastic bags, food packaging, and stretch films
2. Injection Molding LDPE
Applied in bottle caps, plastic containers, and industrial parts
3. Extrusion LDPE
Used for making plastic films, flexible pipes, and wire and cable coatings
4. Blow Molding LDPE
Suitable for manufacturing lightweight plastic bottles, storage containers, and plastic tanks
5. Coating Grade LDPE
Used in paper laminates, moisture-resistant packaging, and protective coatings



Applications of LDPE in Various Industries
Thanks to its diverse physical and chemical properties, LDPE is widely used in multiple industries:
Packaging: Plastic bags, protective films, and food packaging
Agriculture: Greenhouse films, irrigation pipes, and ground covers
Construction: Waterproof membranes, wire and cable coatings, and flexible pipes
Medical Industry: Disposable syringes, pharmaceutical packaging, and medical supplies
Automotive Industry: Interior vehicle components and waterproof materials for insulation
Advantages of Using LDPE
High flexibility and impact resistance
Low production cost compared to other plastics
Recyclability, reducing environmental impact
Good chemical resistance against many acids and bases
Disadvantages of LDPE
Low heat resistance, causing deformation at high temperatures
Sensitive to UV radiation, leading to degradation over time
Permeability to certain gases, which can be problematic for some packaging applications
Lower mechanical strength compared to polymers like HDPE
